News
Author: KIT
During the third semester, researchers from KIT further studied and improved the conditions for the mechanochemical transformation of black mass (BM) into metallic black mass (MBM). Since BM supplied by ACC is already in a reduced state, they focused on reducing BM supplied by TES. This BM consists mostly of NMC (lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides) cathode material and graphite, which was found to slow down the reaction kinetics. The reduction of the cathode active material by the metallic reducing agent result in the formation of the transition metals along with lithium oxide (Li2O) and the oxide of the respective reducing agent, which can be monitored by X-ray diffraction.
In contrast to the previous two semesters, researchers switched from shaker mills to planetary mills, which enable control of the rotation speed and larger volumes that can be processed. Various parameters such as ball-to-sample ratio (BSR), ball size, total load and rotation speed were investigated to optimise for a short reaction time.
Main take-aways
In general, the higher the BSR, the more mechanical energy can be transferred per gram of powder which results in a more intense milling and a faster reaction; however, this limits the throughput. Larger balls, on the one hand, lead to higher kinetic energies. On the other hand, fewer balls are used to keep the BSR constant resulting in a lower collision frequency. The maximum rotation speed is lower to prevent damage to the grinding media.
With Calcium as the reducing agent, no reaction was achieved at all. An unfavorable combination of ductility and size of the calcium pieces seems to resist further size reduction, which is required for the reaction.
Aluminium has the advantage of being used as a current collector and is already present in the black mass. However, during the reaction, LiAlO2 is formed, which is limiting the subsequent Li extraction efficiency in WP5. This problem can be avoided when magnesium is used as the reducing agent, which proved to be more reactive than aluminium but doesn’t form other lithium compounds than Li2O.
Compared to the shaker mill, a higher reaction rate was observed in the planetary mill. Researcher from KIT achieved a complete conversion of the lithium transition metal oxide in the planetary mill within 3 h using Mg as the reducing agent. In a larger version of the mill, the required milling time increases to 8 hours. Here, further investigations are planned for the next months.
Read previous article on the pre-treatment operations: Pre-treatment operations: Reactive milling for the production of metallic black mass
© Photo: Adobe
Author: KIT
Following previous work performed in work package 5, researchers from KIT further investigated the lithium (Li) extraction from black mass (BM) supplied by partners ACCUREC (ACC) and TES.
The BM provided by ACC consists of graphite, as well as transition metals such as nickel (Ni), manganese (Mn), and cobalt (Co), along with their respective oxides and impurities like copper (Cu), iron (Fe) and few fluorinated compounds. Li is present in the form of lithium carbonate (Li2CO3), lithium fluoride (LiF) and lithium aluminium oxide (LiAlO2). However, breaking off lithium aluminium oxide to a soluble Li-salt and removing fluoride contamination proved to be challenging.
Previous work reported the simultaneous incorporation of fluoride ions and decomposition of LiAlO2 using an excess of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) at elevated temperatures. More recent developments of the processes show improvement, especially decreasing considerably the amount of of Ca(OH)2 , while achieving a Li extraction of 87 %. Instead of heating the suspension, it is possible to initiate the reaction by liquid-assisted grinding in a planetary mill. The results show LiAlO2 is decomposed. However, the fluoride content is not efficiently removed.
In the BM supplied by the partner TES, most Li is present as lithium transition metal oxides (LiTMO) and a small amount of LiF. To enable Li extraction, this BM was reduced by reactive milling in Task 4.4 – Reactive milling for the production of metallic black mass (MBM). The obtained MBM consists of graphite, the metallic composite, lithium oxide and the oxidised reducing agent, along with some impurities like Fe and fluorinated compounds.
After investigating aluminium (Al) and calcium (Ca) in the previous steps, researchers at KIT performed tests to assess Li extraction using a magnesium (Mg) system, which presents various advantages, namely: avoiding, on one hand, the formation of Li salts with bad solubility, and relying on the other hand on insolubility of Mg in the high pH aqueous solution.
After aqueous extraction, researchers obtained a mixture of Li2CO3 and LiF. In the upcoming months, this mixture will be purified to a battery-grade material.
During the past years, the increase in the use of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) has become more prominent. An unsurprising trend, whatsoever, due to the widespread and rapid adoption of clean mobility applications, electronic devices, and energy storage systems. Despite their undeniable environmental and social benefits, several challenges lie ahead. In 2022, global lithium demand exceeded the supply despite an 180% increase, IEA reports. Recent communications already forecast the demand of lithium (Li) is expected to soar over the next decade, with mobility accounting for the main consuming market.
The current supply of primary resources is deemed insufficient for the growing demand. Approximately 60% of today’s lithium is mined for battery-related applications, a figure that could reach 95 percent by 2030, McKinsey reports estimate. But this rapid increase in the use of LIBs in EVs will introduce a large quantity of spent batteries in the near future. The alternatives to manage spent batteries include remanufacturing, repurposing and recycling, with the latter one playing a significant role from both ecologic and economic points of view.
Current recycling processes lack selectivity in recovery control and require significant consumption of reagents and energy. The research conducted by the RHINOCEROS partners at Sapienza University of Rome (UoS), Department of Chemistry, aims to develop an electrochemical process for selective extraction of Li from electrodic powder of end-of-life (EoL) LIBs. This concept simulates the charging process of a LIB with an aqueous electrolyte and a cathode material (counter electrode) that facilitates water reduction. The hydroxyls freed by water reduction and the Li + cations deintercalated by the anode will form a LiOH solution.
Using two samples – a commercial powder, respectively one coming from EoL LIBs, and testing the delithiation process using various parametres, UoS researchers obtained:
- Li extraction of 99% from commercial powder
- Li extraction of 82% from waste powder
The lower Li extraction on EoL electrode powders compared to commercial ones is due to the presence of SuperP [a high purity and structured carbon black powder with a moderate surface area for the lithium-ion industry], which oxidises under delithiation conditions.
Discover the scientific publication
Europe stands at a turning point in its journey towards establishing a competitive European value chain for batteries. Important steps have been taken in encouraging battery manufacturing plants, only to mention here the inauguration of the first gigafactory by Northvolt in Sweden. Yet, the market demand for batteries continues to surge, fueled not only by the electric vehicle sector but also by other mobility applications and stationary storage needs. The recently launched Quarterly EU Electricity Market Report Q3 ’23 indicates over 600,000 new battery electric vehicles (BEVs) were registered in Q3 ’23, 36% higher than the corresponding quarter in 2022 and counting for 24% market share.
In response to these record demands, the European batteries research and innovation (R&I) community has been dedicated to supporting the establishment of this industrial value chain in Europe, aided by public funding, including by the European Union. Various R&I projects under the umbrella of the BATT4EU Partnership (established under Horizon Europe Programme in 2021), RHINOCEROS included, are sharing forces within the Cluster Hub “Production of materials for batteries from European resources” to address common challenges.
Motivated by the global geopolitical developments, the strategic role batteries play in achieving Green Deal objectives and the ever-evolving nature of battery technologies, Europe recognises the critical need for strategic alignment among stakeholders. Replacing the BATT4EU SRIA of 2021 and the Batteries Europe SRA of 2020, the 2024 SRIA outlines key strategic actions that the European Batteries R&I Community will undertake to advance collaborative research projects facilitated by the BATT4EU Partnership. Different from the previous strategic agendas, the 2024 roadmap goes beyond specific chemistries, leveraging also the power of disruptive (digital) technologies to advance research across all battery types, including material science, manufacturing and recycling processes.
The new agenda draws on the roadmaps published by Batteries Europe and Battery 2030+, compiling inputs from numerous European battery experts, offering recommendations on short, medium, and long-term objectives. It emphasises the need for coordinated action not only at the European level but also within national and regional programmes.
The 2024 SRIA points to the following six imperatives which are necessary to set the foundations and support a competitive battery value chain in Europe:
• Ensure that (BATT4EU) research results reach gigafactories and the markets, through pilots, demonstrators and improved decision making aided by digital tools.
• Increase the strategic autonomy of Europe by reducing the reliance on foreign critical raw materials by supporting local and circular supply chains and support research into different battery chemistries, including sodium-ion technologies.
• Improve battery affordability to accelerate the green transition and keep the European industry competitive by improving batteries based on materials that are more abundant and pushing for better integration into end-use applications.
• Improve the flexibility of battery manufacturing and recycling systems to reduce lock-in effects and respond quickly to changes in a rapidly developing industry.
• Implement a safe and sustainable by design framework for batteries, which plays to European strengths, and which will help reduce emissions and use of substances of concern, improve safety and allow for the integration of smart functionalities.
• Support the continuity of excellent European battery research and academic-industrial cooperation by improving access to research facilities and pilot lines, use research projects to build up a skilled workface, and by avoiding gaps in research through continued funding, which will bind talented researchers to Europe.
Interested in finding out more information about the recently released SRIA?
BATT4EU Partnership is organising a webinar on 20 March 2024, between 10:00 and 11:30 Brussels time. The aim is to present the official document and to host engaging discussions with the experts behind this publication who will explain how this document will redefine the dynamics for the European battery sector.
Register here
RHINOCEROS attending Shifting Economy Week
From 21 to 25 November 2023, the city of Brussels hosted the Shifting Economy Week, an annual event dedicated to showcasing transformative projects that aim to pave the way to an economy that is low-carbon, regenerative, and equally circular. The 2023 exhibitors’ line-up included, among other regional stakeholders, our partner Watt4Ever (W4E), industrial partner specialised in the development of innovative solutions for energy storage and management. W4E leveraged its presence at Shifting Economy Week to to raise awareness about the importance of circular economy principles in the context of the battery industry.
During the same event, W4E’s CEO, Aimilios Orfanos, was invited to speak at the BeCircular conference, an event dedicated to presenting concrete examples of circular economy approaches put in place by Brussels-based companies. He shared insights from W4E’s experience in developing second-life battery systems for electric vehicles, emphasising their potential benefits in terms of environmental impact and cost savings. Simultaneously, the CEO also highlighted the challenges faced by the industry in implementing circular business models, including regulatory barriers and market incentives.

RHINOCEROS at its second participation at Circular Wallonia Days
A few days after attending Shifting Economy Week, W4E represented the RHINOCEROS project at the Circular Wallonia Days, held on 13 and 14 December 2023. Centred around advancing the circularity of the batteries value chain, the event brought together stakeholders from academia, industry, and government to discuss strategies for improving the sustainability of battery production, use, and disposal. The focus topics covered recycling technologies, supply chain transparency, and policy measures to support the transition to a circular battery economy.
© Photo credits: Watt4Ever
Despite a different objective, the RHINOCEROS project partners have shown growing interest in the Digital Battery Passport, an initiative of FREE4LIB, a sister project from the Cluster Hub “Production of raw materials for batteries from European resources”. This collaboration shows our commitment to contributing to the European battery community through the exchange of knowledge and experience.
The FREE4LIB workshop had a three-fold objective, including a brief presentation of the preliminary results of the battery passport concept development, the outline of the implementation challenges and potential follow-ups of industrial scale-up, and the clear differentiation between battery second use (B2U) versus recycling. The event drew approximately 50 participants from various segments of the battery value chain, which ensured a comprehensive and multifaceted perspective of the subject matter.
The introductive session presented the FREE4LIB project, briefly highlighting past achievements and focusing mainly on the remaining activities outlined in the workplan. The following session was led by Julius Ott (industrial engineer with expertise in circular economy at Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz). During the past year, researchers at Univ. of Graz worked on finalising data collection and processing related to the development of a data model of the digital passport platform which aims to close the information gap between beginning-of-life (BoL) and end-of-life (EoL) battery lifetime. This interactive session turned out to be an appropriate opportunity for researchers at Univ. of Graz to present the outcomes of their data collection and handling, and to evaluate their relevance within the reality portrayed by the workshop attendees.
Participants, predominantly familiarised with the EU-funded battery projects, confirmed the findings reported by Univ. of Graz. However, they also raised concerns about data sharing. The outcomes of the interactive session, complementing prior research, will serve as valuable guidance for the FREE4LIB project in implementing the battery passport within their project.
For additional background information on the digital passport developed by FREE4LIB, please refer to previous articles.
On Thursday, 16 November, during the 2023 edition of the Raw Materials Week, the twelve EU funded projects that constitute the Cluster Hub ‘Materials for batteries’ gathered for their annual event in Brussels.
The Cluster Hub has been initiated last year during the 7th edition of the Raw Materials Week. The main objective of the meeting was to meet and discuss the latest developments in the participating projects as well as the new challenges and opportunities discovered through the projects’ lifetime. Nader Akil, Operations Manager at PNO Innovation, inaugurated this second edition outlining the motivation behind the hub’s establishment. He underlined the positive reception and sustained interest from various stakeholders keen on joining this initiative.
Discover and/or rediscover the first edition of the Cluster Hub workshop
Co-organised by RELiEF, EXCEED, ENICON and RAWMINA, the event was also the opportunity to welcome the four new members of the Cluster (EXCEED, RAWMINA, METALLICO and CRM-geothermal). the workshop gathered nearly 100 organisations driving the production and the recycling of raw materials for battery applications from primary and secondary resources.
Building on the initial objective of creating an environment that could foster knowledge exchange on different approaches for the recycling and recovery for battery applications, the event focused on three major topics that depict the transversality characterising the projects: the raw materials through research and science, the roles and challenges of industry and market for raw materials, and the raw materials under the scope of sustainability, durability and social acceptance. During this annual meeting, an interactive session led by Anish Patil from TechConcepts and representing the RELiEF project had the objective of Mapping the European battery material recycling landscape – more details to be found below, in the section referring to the interactive session.
Research and science unlocking new opportunities in raw materials
The first session was moderated by Sonia Matencio from LEITAT, representing the RAWMINA project. This session had the objective of discussing the raw materials through research and science, under the scopes of mining, refining, processing as well as the battery data. Sonia introduced this topic under the scope of RAWMINA, explaining the integrated innovative pilot system for Critical Raw Materials recovery from mine waste in a circular economy context. To this end, Christophe Aucher, from LEITAT as well, highlighted the need on an open battery passport system to better reflect and account for any adaptations that might be required due to the changing regulatory landscape.
Sonia welcomed afterward Brecht Dewulf from KU LEUVEN and representing ENICON, who discussed the sustainable processing of Europe’s low grade sulphidic and lateritic Ni/Co ores and tailings into battery grade metals. The idea behind this was to show all the potential of Ni/Co resources for Europe.
Xochitl Dominguez from VITO concentrated her speech on gas-diffusion electrocrytallisation (GDEx), a crucial topic for the projects LiCORNE and RHINOCEROS she works with. GDEx is an electrochemical process of reactive precipitation of metals in solution with oxidising or reducing agents produced in-situ by the electrochemical reduction of a gas, in a gas-diffusion electrode. This was followed by Katrin Kieling from GFZ Potsdam, working there for the CRM-geothermal project and shortly explained the challenges of extracting critical raw materials from geothermal fluids. To conclude this first session, Sandra Pavón from Fraunhofer IKTS explained the demonstration of battery metals recovery from primary and secondary resources through a sustainable processing methodology in the METALLICO project.
Discover presentations from Session 1
Insights from stakeholder perspectives: Interactive session on key EU Policies and priorities
The annual meeting followed its course with an interactive session led by Anish Patil, which scrutinised stakeholders’ perspectives on the Green Deal Industrial Plan, Net Zero Industrial Act, Critical Raw Materials Act and the European Battery Regulation 2023. Mentimeter facilitated this interactive session, engaging the audience to explore how these policies intersect, complement each other, and identify critical measures and incentives for achieving their objectives.
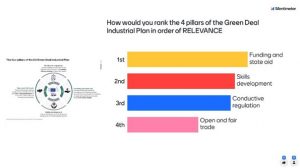
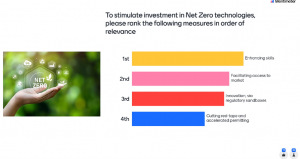
Over 30 persons participated in the live-poll proposed, which results display the priority to be set on funding and state aid regarding ranking the four pillars of the Green Deal Industrial Plan in order of relevance (followed by skills development, conductive regulation, and open and fair trade). Another major topic regarding the stimulation of investment in net Zero technologies, the majority of answers placed the ‘enhanced skills’ as first priority, shortly followed by facilitating the access to the market.
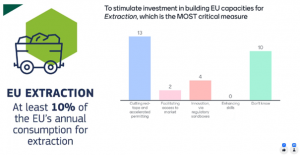
Lastly, the participants were divided regarding the critical measures to implement in the EU to stimulate investment in building domestic capacities for extraction of critical raw materials (CRMs). Although the majority opted for ‘cutting red-tape and accelerated permitting’, approximately half of the answers evoked uncertainty, which emphasised one more time the need to engage with policy makers as external stakeholders in all projects.
Navigating the nexus: industry challenges, market dynamics, social acceptance and sustainability
This interactive workshop was followed by two sessions, which aimed at discussing the challenges and opportunities of raw materials within the frame of industry and market, as well as the social acceptance, sustainability, and durability.
Alan Gonzalez from PNO Innovation Begium, representing LiCORNE, moderated the industry part, whereas Sam Hoefman from RELiEF moderated the last session on social acceptance, sustainability, and durability. Distinguished panellists took the stage to engage in debates on various topics.
Edvarts Emerson, Production and Testing Engineer at Watt4Ever, presented his work on the benchmark depository of 2nd life use of lithium in batteries, acceptance criteria and guidelines, work developed within the RHINOCEROS project. Benjamin Wilson, representing the RESPECT Project, displayed Aalto University’s work advancing efficient, sustainable, innovative and safe battery recycling processes in the EU. Laura Kainiemi from LUT University, representing the RELiEF Project, Konstantinos Komnitsas from the Technical University of Crete (TUC), on behalf of EXCEED, and Vitor Correia from INTRAW for the CRM-geothermal project, collectively debated the role and impact of social acceptance among affected communities, the importance of triggering new dialogues on responsible mining activities, and the joint involvement of regional, national and European authorities, academia, industry partners, and citizens in shaping these initiatives.
A big thank you to all participants for this co-creative and very constructive and inspiring meeting.
Discover presentations from Session 2
Discover presentations from Session 3
The modified Black Mass (BM) obtained in Task 4.4 – Reactive milling for the production of metallic black mass (MBM), as well as the BM supplied by partner ACCUREC (ACC) were leached under different conditions to extract lithium (Li) salt.
The BM provided by ACC consists of graphite, as well as transition metals such as nickel (Ni), manganese (Mn), cobalt (Co), along with their respective oxides and impurities – copper (Cu), iron (Fe), and few fluorinated compounds. Li is present in the form of lithium carbonate [Li2CO3] and lithium aluminium oxide [LiAlO2 ]. However, breaking off LiAlO2 to a soluble Li-salt and removing fluoride contamination is a challenging process. To overcome this, the BM was heated with calcium hydroxide in deionised water for one hour and then filtered.
Illustrated in the next figure, LiAlO2 decomposes during heating and transforms into insoluble calcium aluminium hydroxide. Dissolved fluoride anions are caught by Ca2+ ions and precipitate as calcium fluoride. The soluble part only contains Li- and Ca-salts. The latter can be transformed into calcium carbonate and removed with a second filtration step.
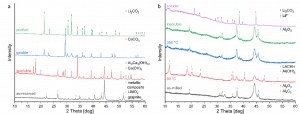
X-ray diffraction patterns of leaching and purification process. a) black mass supplied by ACC and treated with calcium hydroxide. b) aluminium system of modified black mass
The second BM from partner TES, obtained after ball milling, consists of graphite, the metallic composite, lithium oxide and the oxidized reducing agent, along with some impurities like Fe and fluorinated compounds.
Lithium extraction after ball milling
In the aluminium system, the extraction of lithium salt poses certain challenges. Due to the tendency of residual aluminium powder to ignite when in contact with air, this requires cautious handling. During milling lithium aluminium oxide is formed, and in the basic solution, a significant amount of aluminium hydroxide dissolves and reacts with lithium hydroxide and CO2, resulting in the formation of a poorly soluble compound called LACHH. To address this problem, the suspension is heated to 90°C to reinforce the reaction between aluminium hydroxide and lithium hydroxide. The LACHH formed can be decomposed at 350°C into insoluble aluminium oxide and soluble lithium carbonate, which can be separated through filtration.
Lithium extraction in the calcium system, on the other hand, is a relatively straightforward process. The milled powder shows low reactivity towards both oxygen and water. Scientists successfully extracted 98% of lithium from the black mass; however, calcium hydroxide was also dissolved in the process. Subsequent purification steps led to the isolation of lithium carbonate with a purity of 93% in a yield of 75%. The main impurities are shown in the figure displayed below.
In the upcoming months, researchers will work to improve the leaching conditions towards a lower reagent and water consumption, while obtaining a higher purity of resulting lithium salt and lower lithium loses during purification steps.

Impurity cations in isolated lithium carbonate from the calcium system of modified black mass
During the second semester, researchers from KIT further studied and improved the conditions for the mechanochemical transformation of Black Mass (BM). With the BM supplied by ACC is already in a reduced state, the focus now shifts towards reducing the BM provided by partner TES.
This BM consists mostly of nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) cathode material and graphite, and it was found to cause a longer reaction time. It is expected that the graphite exfoliates during milling and creates thin protective layers around NMC particles and the reducing agent, slowing down the reaction kinetics.
Using variations of milling parameters like ball-to-sample ratio or the type and amount of reducing agent, researchers optimised the process towards the fastest kinetics. During the investigation, no intermediate reduction to transition metal oxides in lower oxidation states was observed. However, the full reduction of the respective part to the metallic composite occurred.
The operation took place in a shaker mill, and it requested an excess of 3.3 equivalents of Aluminium (Al) towards NMC was required to attain a complete reduction within a reasonable time. This transformation was accompanied by the formation of aluminium carbide and the presence of residual fine aluminium powder which caused a self-ignition hazard when the milled powder came into contact with air.
In contrast, when using calcium as a reactive agent, researchers observed a fast reaction but they also reported a strong dependency of reaction kinetics on calcium size. The hazard of self-ignition when exposed to air was limited in this case by using stoichiometric amounts.
In addition, the research team has been conducting preliminary experiments for the scale-up process using a planetary mill. It was observed that the choice of the milling type has a significant impact on the reaction kinetics. Attempts to crush calcium pieces proved to be unsuccessful, therefore not initiating any reaction. However, when using aluminium, reactions occurred much faster.
In the months ahead, the research team working in WP4 will continue to investigate the milling parameters for the planetary mill.
Find out more information about the activities developed in WP4 in the article Reactive milling for the production of metallic black mass (MBM) – Rhinoceros project (rhinoceros-project.eu)
Read more about the black mass leaching operations in the article Materials extraction and direct routes for the synthesis of electrode materials: Recovery of Lithium as battery grade materials
Three dimensional (3D) Scanning of Battery Packs
Following the manual dismantling of various battery packs during the first six months of project, researchers at University of Agder (UiA) have developed a semi-automated process to address the diverse nature of battery packs. Their advanced robotic system can estimate the size of individual components of a battery pack. Afterwards, using different angles, it identifies optimal locations to capture precisely 3D images of these components, thus ensuring no detail is missed through this comprehensive scanning.
Using different perspectives, this thorough scanning process is further translated into a list of point clouds. Applying sophisticated algorithms, these point clouds are later combined and merged into a solid mesh component. This process is repeated individually for each new component which needs to be scanned.
Beyond geometric characteristics
While geometric characteristics are important, they provide even greater value when combined with other physical attributes and interconnection data of the components. The researchers have successfully documented these details, resulting in a rich digital repository of the battery pack. With the establishment of this detailed digital repository, the focus is now shifting towards its applications, where the primary goal is to automate the disassembly sequences.
Simultaneously, the team is also focusing on the automatic characterisation of battery packs and modules. Significant efforts are channeled towards creating a robust digital simulator, which will serve as a platform for training and rigorous testing of the disassembly planner – currently under development.
Innovation in disassembly tools
At the same time, the research team involved in work package 3 have been working on improving the disassembly operations tools. The results reported positive feedback, with several tools already successfully tested in lab environment. This is a significant step towards the fully automated disassembly process.
A noteworthy development is the automation of the non-destructive disconnection of cables. This procedure is essential as it stands as the second most frequent operation in battery pack disassembly, just after the unscrewing operation.
You can read more about previous activities developed in work package 3 in the article ‘Manual dismantling of a battery pack‘.