News
The last consortium meeting included a session dedicated to ongoing clustering activities, where the RHINOCEROS partners invited the RESTORE project coordinator, Christophe Aucher, Area Manager Energy Storage at LEITAT. The objective of this initiative is to introduce the two EU-funded projects, both focusing on advancing battery material treatment and recycling technologies. Both projects are members of the Cluster Hub “Production of raw materials for batteries from European resources”.
The RESTORE project introduced its approach to treat black mass – from sorting to discharging, retrieving all available materials and validating them in a coin battery. This concept aligns closely with the philosophy of the RHINOCEROS project, emphasising the importance of contactless sorting and efficient battery discharge processes. The aim of RESTORE is to remove cables and discharge batteries within 40 minutes, which would bring a big step towards more efficient recycling processes.
During the event, representatives of both projects addressed various industry challenges. One major issue is the profitability of selling black mass to states outside of EU, compared to the domestic scenario for producing electrodes. Additionally, the European market faces a slowdown in battery production, showing citizens preference for hybrid cars over electric vehicles. Nevertheless, both sides agreed on the need for critical raw materials, indispensable to emerging industrial sectors, underscoring the importance of sustainable and efficient recycling processes.
The RESTORE project introduced several technological advancements, including the KYBURTZ cell-to-electrode direct recycling method developed by VITO. This method aims to streamline the recycling process and enhance the quality of recovered materials.
Although the two projects share similar objectives and consortium partners, technical questions were not missing, addressing mainly the electrochemical recovery of lithium, the impact of the aqueous media on the quality of retrieved material and the potential to work in batch mode.
This first online encounter of RHINOCEROS and RESTORE sparks a lot of curiosity, key ingredient of innovation and technological advancement. Prospects already show opportunities to stimulate collaborations and knowledge exchange in the battery recycling R&I field.
Researchers at the Faculty of Engineering and Science within the University of Agder [UiA] have developed a digital simulator along with an algorithm that automatically generates the Disassembly Process Plan [DPP] for batteries. The algorithm is built to select autonomously the most suitable machine to execute each disassembly operation, along with the corresponding toolkit. Beyond automating the DPP, this technological breakthrough promises to reduce the total disassembly process duration.
With the electrification of mobility, the upcoming wave of e-waste will be hard to deal with. In general terms, electrical waste is shredded in bulk before sorting and reprocessing. But lithium-ion batteries [LiBs], the types used in EVs, are inflammable and request careful handling. Moreover, shredding lots of different types of e-waste simultaneously inevitably results in contamination. Separating components before shredding would yield greater levels of purity, even allowing various components, such as cathodes, to be reused in their entirety. Dismantling batteries is a dangerous operation due to the risk of fire or explosion. Nonetheless, this process typically involves manual labour to remove the casing and separating the internal components – electrodes, electrolyte, cabling and separators.
Within the RHINOCEROS project, the UiA is responsible for developing an automated system for characterising battery state, discharging via the grid and dismantling for reuse or recycling. Their ultimate goal is to reduce the operational duration and to improve resource utilisation. An important phase of their work lies in the development of a Disassembly Process Plan – shortly DPP, which features a disassembly sequence plan [DSP] and an algorithm that can establish autonomously the most suitable equipment for each disassembly operation. To avoid several rounds of unsuccessful trials, researchers have firstly created a digital simulator where they already tested the algorithm generating the DPP.
Trained to use time and resources efficiently
The use of a simulation environment offers a safe and cost-effective way for researchers to test and refine the algorithm in a controlled context. Beyond safety and resource optimisation, simulators facilitate also scalability and reproducibility. The algorithm is trained to select the most suitable toolkit and calculate optimal tool change sequences, which reduces the overall disassembly process duration. Moreover, it also features integrated data that allow it to verify beforehand compatibilities between requested tools and machine capabilities. By determining optimal disassembly sequences and tool allocation, the DPP reduces operational costs through more efficient equipment usage.
Closer look at the technical specifications of the DPP developed in RHINOCEROS
From a technical point of view, the digital simulator, built on a foundation of Python and NumPy, tracks job progress, machine availability, tool states and temporal dependencies. Researchers applied various Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms, including Proximal Policy Optimisation (PPO), Policy Gradient (PG), Advantage Actor-Critic (A2C) and Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic (A3C), to solve the Job Shop Scheduling Problem (JSSP). The PPO algorithm, in particular, has demonstrated superior performance compared to other algorithms and state-of-the-art (SoA) solutions. The simulator is using datasets similar to the battery disassembling problem, mimicking real use case scenarios.
In a recent development, researchers have introduced an innovative approach called QTM (Q-learning with Tsetlin Machines) to improve scheduling algorithms. This new method combines the pattern recognition abilities of Tsetlin Machines (TM) with the decision-making strengths of Q-learning. The QTM approach uses a sophisticated reward system to balance the completion of tasks, minimize the time taken, and optimise the overall schedule. The TM component excels at identifying patterns in scheduling scenarios by analysing key features of jobs and operations. Meanwhile, the Q-learning framework provides a foundation for learning through a process of trial and error, gradually improving decisions over time.
The DPP developed in the RHINOCEROS project features PPO, QTM and classic deep Q-learning.
Impact on the real-world industrial applications
The DPP brings significant implications for real-world applications, particularly in industries that prioritise efficiency and sustainability. In EV battery recycling, it optimises the disassembly sequence, enhancing efficiency. It is also applicable to electronics WEEE recycling, where complex assemblies require precise disassembly. The DPP can integrate into large industrial scales, enabling the reuse of valuable components and supporting circular business models.
Automation integrators and robotic system developers benefit from the DPP’s computational framework, which models tool-changing operations and associated costs, optimising robotic movements and tool selection. Academic institutions can use the DPP to study broader questions in automated planning and robotic intelligence, providing a well-defined problem structure for testing new algorithms and heuristics.
For industrial research labs, the DPP offers a framework to develop specialised applications across different product categories, evaluate alternative product designs for end-of-life processing efficiency and simulate different disassembly strategies before physical implementation, reducing development costs and accelerating innovation cycles in recycling technologies.
Future developments for the Disassembly Process Plan
Plans for the DPP foresee its integration into a comprehensive digital twin of the manufacturing environment. Before its demonstration in a real-world setup, this digital twin operating with configurable tool capabilities and interdependent job sequences, will have to pass thorough testing in a simulated environment.
© Visual: University of Agder [UiA]
Lithium-ion batteries proved to be one of the most efficient energy storage solutions, widely used for applications such as electric vehicles [EVs] and renewables. Despite faltering economies and material shortages, more than 40 million EVs are expected on the EU’s roads by 2030. With mass electrification of transport, there will be an important demand for batteries and the materials they are made from. Despite an incentivising regulatory context at EU level, in 2023 Europe was home to only 1% of the production of key battery raw materials. European carmakers and battery cell producers are already fret about volatile prices and limited supplies of cathode and anode materials. But with EV fleet number growing on the EU’s roads, the volumes of End-of-life [EoL] batteries will considerably increase in the near future. And so will the pressure to recycle closer to home, recovering key components and mitigating the supply chain risks.
Conventional recycling methods often require high consumption of energy and reagents. But electrochemistry offers a promising green alternative method, enabling selective recovery of Li without the need for chemical extracting compounds.
Selective electrochemical extraction of lithium
Researchers at Chemistry Department of Sapienza University of Rome [UoS] tested various electrochemical parameters to optimise Li extraction from both commercial cathode material and the black masses [BM] obtained by the mechanical pre-treatment operations conducted in work package [WP] 4.
The electrochemical tests on high-purity commercial cathode materials [LiMn2O4, LiCoO2 and LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2] allowed a selective extraction of Li up to 98 %. UoS researchers later applied the same electrochemical process on the black mass recovered by the mechanical pre-treatment, obtaining a lower Li extraction yield of 82 %. This decreased yield was mainly attributed to the presence of conductive carbon which undergoes a simultaneous electrochemical oxidation. Analysis of the resulting electrolyte at the end of delithiation experiments showed negligible extraction of cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), and manganese (Mn). This demonstrated the method’s ability to selectively extract Li without causing the dissolution of other cathode elements.
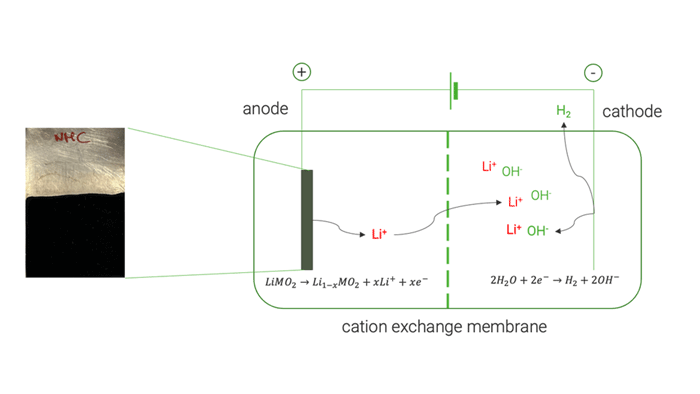
Cation exchange membrane | © Univ. of Sapienza
The optimised electrochemical conditions applied on the BM were replicated in a two-chamber cell to facilitate the separation and concentration of extracted Li on the cathode side, achieving approximately 85 %. The resulting solution was used to crystallise LiOH, resulting in a mixture of LiOH and LiOH·H₂O, with a purity exceeding 99.5 %.
Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and Li-Mn rich cathode material
The direct synthesis of high-value products from EoL LIBs, bypassing the complex and expensive separation of different metals, can be achieved through a competitive recycling strategy. The simultaneous synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and lithium-manganese-rich (Li1.2Mn0.55Ni0.15Co0.1O2 – LMR) cathode material from EoL LIBs represents a promising approach to enhance the economic feasibility of hydrometallurgical recycling processes by producing high-value-added advanced materials.
UoS researchers developed an innovative recycling process to directly synthesise a layered LMR cathode and rGO from EoL LIBs. The proposed recycling strategy relies on the application of Hummers’ method to process the electrodic powder delivered by pilot-scale mechanical pre-treatment of mixed Li-ion batteries. The Hummers’ method has allowed for the quantitative extraction of metals from the electrodic powder and the production of GO without any metal impurity. The resulting solution contains the metals from the cathode materials (Co, Ni, Mn) with a significant amount of manganese from the KMnO4 used in the Hummers’ method. From such consideration stems the idea to synthesise LMR cathode material.
UoS researchers synthesised GO using the black masses obtained from three distinct EoL LIB pretreatments performed in WP4. The effects of thermal, mechanical and mechanochemical pretreatments were evaluated using the widely adopted Hummers’ method for graphene production. The study conducted by UoS researchers examined both pristine black masses and those subjected to metal removal via conventional acid leaching, a process frequently employed in LIB recycling to extract metals from cathode materials. This metal removal procedure had a notable effect on introducing oxygen functional group defects across all samples. A synergistic effect was particularly evident in the mechanochemically treated black mass, where acid leaching increased the GO yield significantly. This remarkably high graphite conversion to GO underscores the importance of selecting appropriate pretreatment methods for EoL LIBs, particularly when aiming to integrate advanced materials like GO into the recycling process.
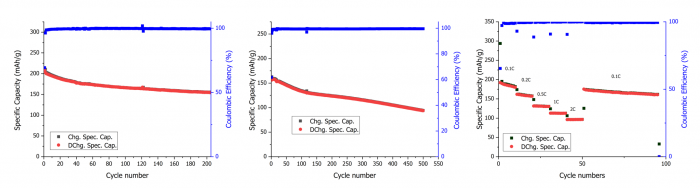
Cycling performance of LMR synthesised from thermally treated black mass: (a) Galvanostatic cycling at 0.1C, (b) Galvanostatic cycling at 1C, and (c) Rate capability performance with the current increasing from 0.1C to 2C every 10 cycles | © UoS
Recovery of Ni/Co materials by solvometallurgical route
RHINOCEROS is a research project that aims to o create economically and environmentally sustainable methods for reusing and recycling LIBs. The project focuses on developing cost-efficient, flexible and eco-friendly processes to recycle all materials in LIBs, including metals, graphite, fluorinated compounds and polymers.
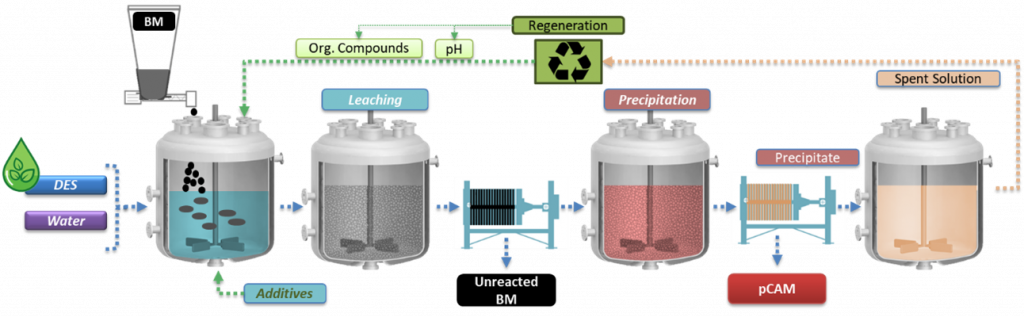
Flowsheet of the leaching, precipitation and regeneration process | © TEC
After studying the effects of the pre-treatment processes applied in WP4 to generate BM, researchers at TECNALIA [TEC] tested various solvometallurgical routes to extract critical metals like Ni, Mn and Co from LIBs under mild conditions. They established optimal process conditions to achieve leaching and precipitation efficiency along with high purity of the produced precursor of cathode active materials (pCAM) under mild conditions. This approach also enhances the recyclability of the extractant.
After characterising all the input materials received from the pretreatment operations, TEC research group analysed also the obtained leachates. The leaching process was optimised at laboratory scale by studying the effects of various parameters such as leaching time and temperature, stirring, waste/liquid ratio and additives.
The solvometallurgical process for recycling end-of-life [EoL] battery BM has successfully developed high-yield, selective systems, validated across various NMC chemistries and black mass pretreatments, achieving over 95 % leaching efficiency. Controlled precipitation delivered up to 95 % precipitation efficiency, producing precursors with more than 99 % purity, meeting project targets. Moreover, researchers have confirmed the scalability of the solvometallurgical process to large-lab testing without performance loss. To address the costs of this process, TEC researchers have also investigated alternatives to reuse and recycle the deep eutectic solvent [DES] leaching spent solution, reporting its dependence on the properties of the BM feed.
The residue after leaching – the graphitic anode material – has been purified via hydrometallurgical routes, underscoring the difficulty of removing the most refractory phases resistant to harsh leaching conditions.
Optimised recovery of materials from low concentration waste streams
A different task in the refining work package, led by LEITAT and TEC, aims at the recovery of low concentration materials from leachates and effluent streams produced in previous refining tasks. It is divided in three subtasks, each exploring different membrane-based technologies to achieve a zero-waste strategy for recovering remaining elements.
The objective of the first subtask is to develop new extractants based on ionic liquids or DESs, to be used within novel Polymer Inclusion Membranes (PIMs), for the recovery of Li from solvometallurgical refining final streams. The team firstly analysed the SoA on Li extraction strategies, selected, synthesised and characterised different potential extractants based on hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (HDESs). Selected HDESs were synthesised and sent to the next subtask devoted to PIM fabrication and testing using different ILs and/or synthesized HDESs. These membranes represent an innovative technology that effectively adapts to the specificities of each input stream, enabling optimal recovery of valuable metals present in the waste generated by processes carried out. In the this subtask, the PIMs yielded the following recovery rates:
- Co and Mn: efficiencies close to 80 %
- Ni: 60 % recovery
- Li: only 19 %, but exhibiting a high flux rate of 1.2 mol/m²·h, suggesting potential for larger lithium recovery.
Finally, in the last subtask, researchers developed a three-chamber electrochemical process for the extraction, concentration and recovery of lithium in the form of lithium carbonate from solvometallurgical final streams. Different ion-exchange membranes were characterised and lithium carbonate precipitation step was studied and optimised. They tuned the overall process conditions achieving more than 70 % Li extraction from leachate to catholyte and high lithium carbonate precipitation yields (>70 %) with high purity (>94 %).
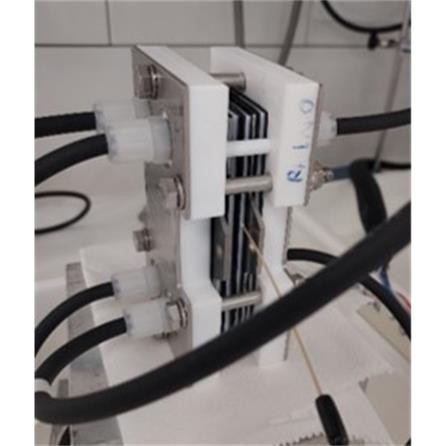

Three-chamber electrochemical cell | © TEC
Extraction of Ni/Co/Mn/Li with GDEx
Gas-diffusion electrocrystallisation [GDEx] is an innovative electrochemical process used to recover metals from complex fluids, such as leachates, industrial waste streams and organic solutions. This innovative process has been successfully demonstrated in multiple research projects, proving its capability to recover valuable metals while operating under low-cost and environmentally friendly operating conditions. The GDEx process has achieved Technology Readiness Level [TRL] 3 for the recovery of Co and Mn from synthetic solutions and attained TRL 4 in treating black mass leachates. One of the multiple advantages of this electrochemical process is its capacity to recover Ni, Co and Mn simultaneously, with the flexibility to manipulate operational conditions to obtain targeted products.
Specifically for the battery recycling sector, the GDEx process offers various advantages over conventional battery recycling methods:
- High recovery efficiencies, exceeding 90 % for Co and Mn and over 90 % for Li, with potential for further optimisation.
- Low energy consumption: less than 20 kWh per kg of recovered material, which reduces the operational costs significantly.
- Minimal chemical input: the process relies primarily on air and in-situ synthesised oxidising/reducing agents, ensuring high material efficiency and circular use of non-hazardous chemicals.
- Mild emissions, with the possibility to further treat any effluents using conventional wastewater treatment methods.
- Low temperature operation: from room-to-mild temperatures [18 – 70 °C].
- Direct synthesis of functional battery materials, such as Co/Ni/Mn spinels and birnessites, which can be used to manufacture new lithium-ion battery electrode materials and eventually LIBs. This feature eliminates the need for additional refining steps, streamlining the production of new batteries from recycled material.
Within the RHINOCEROS project framework, researchers at VITO have been finetuning the operational parameters of their proprietary GDEx process, additionally testing and validating the recovered materials through the synthesis of high-performance electrodes for next generations batteries, demonstrating therefore the circularity, cost, environmental and social benefits of the solutions developed.
After testing the direct recovery route of Co, Ni, Mn and Li on synthetic solutions with the main objective to finetune the GDEx operating settings, VITO researchers have been implementing the process to the BM samples provided by the pre-treatment operations [ACC and TES] and to the aqueous extractants processed by the hydrometallurgical route explored by UoS and the solvometallurgical route explored by TEC. Additionally, they also documented the testing operations using a 3D phase diagram material library, mapping the formation of different materials based on Co/Ni/Mn concentration ratios from synthetic solutions.
The GDEx process applied on the leachate solution obtained from the BM provided by ACC achieved high recovery rates: 90 % for Ni, 89 % for Mn and 96 % for Co.
On the other hand, GDEx process implemented on the leachate solutions provided by UoS [originally from the BM of TES] results in the metal extraction efficiencies of 98 % for Ni, 68 % for Mn, and 96 % for Co. Sequential GDEx experiments have potential to improve the recovery efficiency by removing the impurities first and then the recovering the targeted metals. GDEx treatment on TEC’s leachate solution required optimisation due to the presence of high content of Cu and Al impurities.
With better results obtained on the lithiated nickel manganese cobalt oxide (LNMCO) material synthesised from the leached black mass provided by ACC [thermal pre-treatment], VITO researchers validated its electrochemical activity as a cathode material for LIBs with coin-type half cells. The recycled cathode material maintained a stable charge-discharge profile up to 50 cycles, with an initial charge-specific capacity of 37 mAh g⁻¹ and a reversible capacity of 26 mAh g⁻¹. Later, a batch with large amount of BM will be treated by GDEx process to optimise the electrochemical performance of the recycled electrode material.
After removing the targeted transition metals Ni, Co and Mn from the leachate solutions of the BMs, researchers used the same solution to extract lithium, recovering >99 % Li from the leachate of ACC BM.
The low-temperature or near-ambient operation condition of GDEx process eliminates CO₂ emissions, ensuring a clean and cost-effective approach to recovery of NMC precursor. This aligns with RHINOCEROS project goals, promoting a circular and sustainable battery materials economy. These results highlight the sustainability and scalability of the GDEx process, providing a carbon-free alternative for battery material production, aligning with global efforts to decarbonize critical raw material supply chains.
© visual: VITO
The challenge of recycling lithium-ion batteries
Current battery recycling is confined to recovering raw materials from the scrap produced by gigafactories. But with the adoption of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) increasing, a much richer vein will soon emerge, as the first wave of electric vehicles (EVs) reach the end of their lives. And with it, an additional challenge emerges managing the growing waste generated by these energy storage applications. Traditional recycling methods, such as pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy, have faced certain hurdles in efficiently recovering valuable materials, mainly due to the presence of the organic components present in the battery binders and separators. Some methods are labour-intensive, whereas others need lots of energy or are environmentally harmful. But each hurdle is another opportunity for innovation.
Optimisation of shredding pre-treatment: TES develops and validates their mechanical process for battery recycling
Leveraging over 20 years’ experience in battery recycling, TES partners oversee the development of a shredding process for batteries using its patented in-house technology. Over the first two years of the RHINOCEROS project, they have been conducting various activities using commercial battery packs, from evaluation and deactivation to pack-to-cell dismantling.
TES have been prioritising safety measures and efficiency, ensuring the system extracts the residual energy stored in batteries, preventing it from going to waste. Following the discharge process, TES applies its proprietary mechano-physical pre-treatment, which involves pre-shredding under an inert atmosphere. This is followed by physical separation techniques to recover polymers, base metals (Al, Cu, Fe), and black mass containing valuable active materials such as Co, Ni, Mn, Li and graphite.
Despite the effectiveness of the current mechano-physical treatment, TES has identified areas for improvement. Moving beyond the state-of-the-art [SoA], TES has optimised its process with a pre-drying step to minimise solvent residues and enhance delamination and separation efficiency. These advancements have led to significant improvements in material recovery and product quality, making the recovered black mass more suitable for downstream hydrometallurgical processing.
- Electrolyte recovery rate: exceeding 95 %
- Polymer recovery rate: exceeding 80 %
- Lithium recovery rate: surpassing 95 %, with the majority retained in the black mass
- Impurity levels of Cu and Al: reduced below 1 %
Optimisation of thermal pre-treatment process
However, reintegration of cathodic and anodic materials into the production chain of new batteries remains a challenge. Thermal pre-treatment of the batteries remains paramount in deactivating, releasing and separating the battery materials. But before reaching the thermal pre-treatment, batteries undergo a sorting process according to the cell type. Discharging is not mandatory prior to the pre-treatment.
ACCUREC [ACC] partners have been modifying their thermal pre-treatment process, including a preceding stage for cell solvent recovery, which places their process beyond the SoA. To explore this technological path, they experimented various parameters altering the working temperature and the pressure of solvent distillation, to address safety concerns and stabilise the background electrolyte. A selective recovery of solvent was possible under specific temperature and pressure conditions achieving high purities >99.6 %. However, additional refining steps are necessary prior to further use in battery manufacturing. ACC partners managed to deactivate batteries completely and produce high-purity black mass [BM] with recovery yields of >95 %, using high temperature pyrolysis and a two-stages screening process.
Their process demonstrates that the distillation process prior to the thermal treatment allows the extraction of solvents used in the cell and streamlines high recovery rates of active material. However, their research concludes that the processing of end-of-life [EoL] batteries remains a trade-off between recycling efficiency and purity of the obtained fractions due to the large number of compounds and lack of control over the starting material.
Electrolyte recycling
The safe and environmentally responsible recovery of electrolytes is crucial in the LIBs recycling process. The SoA non-aqueous liquid electrolytes consist of a conductive salt (lithium hexafluorophosphate, LiPF6) dissolved in a mixture of organic solvents and additives. Many of these components are highly volatile, flammable, and classified as toxic. The current state-of-the-art LiB recycling process begins with the production of black mass, obtained through a series of pre-treatment steps. But uncontrolled evaporation of volatile electrolyte solvents during these stages presents major safety hazards. The research group at Technical University of Chalmers [CHA] have been exploring various processing pressure and temperature parameter settings for their supercritical carbon dioxide [scCO2], with a particular focus on the extraction of ethylene carbonate [EC].
CHA researchers successfully developed and validated the scCO2 process for electrolyte recycling from LIB black mass. The results demonstrated a >95 % overall recovery, with individual yields of >99 % for DMC, EMC, and DEC and 95 % for EC, using specific process conditions. The recovered EC retains its original structural integrity, confirming its chemical stability and purity.
But beyond the high purity and selectivity of carbonates, the developed scCO2 does not require any chemical reagents. Moreover, the used CO2 can be indefinitely recycled within the system, turning it into a clean separation process that eliminates toxic gas during processing.
Reactive milling for black mass production
The research group at KIT received black mass samples from partners ACC and TES. Only the samples from TES were fit to study the mechanochemical transformation of BM, as the ACC supply was already in a reduced state. The BM supplied by TES consists mostly of NMC (lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides) cathode material and graphite, which was found to slow down the reaction kinetics.
KIT researchers applied their reactive milling on the BM provided by TES to reduce the cathode material to its metallic form and produce water-soluble lithium salts. They optimised the process using three types of mills [two planetary mills of different sizes and a SPEX shaker mill], engaging three types of reagents: Al, Mg and Ca. They also investigated the influence of milling parameters on the process duration and identified the most optimal parameters for faster kinetics. The planetary mill showed better results than the shaker mill for Mg and Al, while Ca performed well in the SPEX mill.
In depth studies performed by KIT concluded that the process is a mechanically induced self-propagating reaction, which is initiated by mechanical energy, such as the impact energy from the milling balls. Once started, it propagates through the material on its own, similar to a chain reaction. This type of reaction is highly exothermic, releasing a significant amount of heat, which further drives the reaction forward. Small amounts of volatile compounds, such as residual solvents or moisture, were found to have a significant effect on the reaction time. The basis of the volatiles interference is not clear yet, but it seems to be important to remove these compounds before the milling process to ensure a more efficient and faster reaction.
Further experiments are needed to scale up the process and ensure that it can be applied to larger batches.
Vacuum pyrolysis and Supercritical CO2 [scCO2] processing for binders recovery
Binders such as polyvinylidene fluoride [PVDF] and polytetrafluoroethylene [PTFE] for cathodes, and carboxymethyl cellulose [CMC] and styrene-butadiene rubber [SBR] for anodes, are particularly difficult to separate during mechanical processing. This reduces the efficiency of metal recovery and can lead to the formation of environmentally harmful substances, such as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances [PFAS].
Thermal treatment methods, while effective in removing these organics, generate hazardous emissions like hydrogen fluoride [HF] and phosphoryl fluoride [POF3], necessitating stringent gas treatment measures. Additionally, battery separators, often composed of complex polymers like polyethylene [PE] and polypropylene (PP), pose further challenges due to their low economic value and the presence of residual hazardous materials.
ACC has optimised vacuum pyrolysis at 550°C, which enabled the complete decomposition of PVDF, and thus, the effective removal of binders and separators from LIB waste, while recovering fluorinated compounds from decomposition products. Generated HF was captured using two different methods: through potassium hydroxide [KOH] washing (producing potassium fluoride [KF]) or a calcite filter (producing fluorite).
Supercritical carbon dioxide [scCO₂] process technology has emerged as a promising alternative for LIB recycling, offering properties that are adjustable to organic compounds. However, PVDF dissolution in scCO₂ alone requires extreme conditions, making industrial implementation challenging. Chalmers researchers have explored possible co-solvent scCO₂ systems to enable the recycling of binder directly from mechanically treated BM. They developed a specialised extraction process using scCO₂ with a co-solvent (dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO) to recover the PVDF binder from industrial battery waste. The process achieved a 55.6 % recovery rate of PVDF under mild conditions.
The scCO₂ technology was also applied to electrolyte and separator recycling, achieving over 90 % separator recovery with high purity.
© visual: ImageFlow via Adobe Stock
On 12 December 2024, the third edition of the annual workshop of the Cluster Hub “Production of Raw Materials for Batteries from European Resources” took place in Brussels, being co-organised by EU-funded projects RHINOCEROS, CRM-geothermal and CICERO. This third edition, along with an increasing number membership, confirm the hub’s role as a dynamic ecosystem that continues to generate innovations in the European battery materials sector.
The hub’s annual workshop, held as a satellite event of the Raw Materials Week 2024, provided once again a platform for presenting the most promising results from participating projects. Two technical sessions covered the entire battery value chain, from raw materials mining to recycling, while the opening conveniently portrayed the policy, the regulatory and strategic frameworks that support and drive the EU R&I initiatives in the battery sector.
Policy perspectives and supporting mechanisms for the battery sector
Susana Xara, Project adviser on raw materials at European Health and Digital Executive Agency (HaDEA), established the discussions tone, navigating through the insights of the Critical Raw Materials Act [CRMA] and the Net Zero Industry Act [NZIA] and focusing on their contribution to securing a sustainable supply of critical raw materials for the European battery industry.
Wouter IJzermans, BEPA Executive Director, presented the long-term vision and potential revisions of their roadmap, emphasising the importance of policy frameworks and incentives in promoting battery innovation and deployment across Europe.
The presentation of Vasileios Rizos from the Centre for European Policy Studies (CEPS) identified various barriers and challenges emerging from the EU policy framework on batteries, based on inputs from 20 companies across the entire battery value chain, including partners from the BATRAW project, member of the Cluster Hub since 2022. The representative of CEPS concluded with a set of policy messages referring to early dialogue channels established between policy-makers and various stakeholders. Before the legal requirements entry into force, this information exchange on availability of secondary data sets could enable stakeholders to assess the data quality, select suitable sets of information and identify potential data gaps.
Publicly available resources submitted by CEPS:
- Barriers and policy challenges in developing circularity approaches in the EU battery sector: an assessment – CEPS
- Implementing the EU digital battery passport – CEPS
- Compliance with the EU’s carbon footprint requirements for electric vehicle batteries – CEPS
Orchestrating the launch and on-going work of the Cluster Hub, PNO Innovation Belgium [part of PNO Group – leader in innovation and funding consultancy], represented by Dr. Nader Akil, concluded the first session with an overview of all EU funding programmes supporting research, innovation and investment in raw materials production for batteries. Additional to the upcoming funding opportunities and guidance on selecting the appropriate funding opportunities based on the status of technology, Dr. Nader Akil introduced another initiative launched by PNO Group – DIAMONDS4IF. This project supports the preparation of Innovation Fund applications, enabling the transfer of H2020 research results into successful ventures and securing investment funding.
Download Funding Schemes presentation
The third session of presentations commenced with an outline of the main findings of the LIFE DRONE project, which concluded in June 2024. Presented by Lorenzo Toro, process engineer at Eco Recycling, the project demonstrated the feasibility of producing high-quality NMC oxide and graphite from recycled batteries. The innovative process confirmed significant environmental benefits, with a reduction of 59 % in terms of kg CO2 eq. Additionally, one plant is estimated to treat 500 tonnes of batteries/year. The technical-economic evaluation of this industrial plant, with a potential capacity of 500 tons/year, showed a return on investment (ROI) of 31.64 % and a payback time (PBT) of 3.16 years. The analysis indicated that attractive payback times could be obtained even with varying prices for NMC and graphite.
Download LIFE DRONE presentation
RHINOCEROS presenting results of the Electrochemical Li recovery strategy from LIBs black mass
The electrochemical Li recovery from Li-ion battery black mass, investigated in the RHINOCEROS project and presented by Prof. Pier Giorgio Schiavi from Univ. of Sapienza reported Li extraction yields from end-of-life (EoL) LIBs in the range of 82 %, and faradaic efficiency compared to commercial cathode materials (close to 100 %). Researchers have investigated potential causes that could explain the relatively low selectivity ranges of Li and other metals available in black mass. The simultaneous oxidation of impurities found in the black mass can be a justified explanation for the preliminary results obtained. Experimental results show that the extraction percentages for Co, Ni, and Mn remain in very low ranges. When contemplating upscaling scenarios, Prof. Schiavi mentioned the researchers are evaluating an alternative approach that enables the treatment of larger quantities of powder without replicating the manufacturing process of LIB electrodes.
Download RHINOCEROS presentation
The session featured also presentations of other initiatives addressing the batteries recycling topic: Benjamin P. Wilson, Senior Scientist, Hydrometallurgy and Corrosion at Aalto University on behalf of the RESPECT project, Miguel Aguilar, researcher at LEITAT Technological Centre for the BATRAW projects, and Joana Gouveia [Researcher at the Institute of Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Management (INEGI) and America Quinteros [Researcher at LUT Univ.] for the ReLiEF initiative.
The second day of the RHINOCEROS M24 meeting featured the presentation of the TranSensus LCA project, delivered by Prof. Dr. Ing. Thilo Bein. This cross-collaboration initiative aimed to open cooperation activities between the two projects, focusing on the development and application of a harmonised life-cycle assessment (LCA) approach for zero-emission road transport.
Prof. Dr. Ing. Thilo Bein presented the TranSensus LCA project, coordinated by Fraunhofer and launched in January 2023. The project aims to establish a commonly accepted and applied LCA approach for zero-emission road transport while developing a framework based on European data. This initiative involves stakeholders from industry, research, standardisation bodies and the European Commission. The project’s scope could extend internationally, with coordinators planning a wider stakeholder consultation to inform further guidelines and policy recommendations.
Download TranSensus presentation
Potential collaboration routes between RHINOCEROS and TranSensus on LCA topics
The exchange of questions and ideas during the presentation spurred significant interest and facilitated collaboration opportunities between the two projects. The representatives of RHINOCEROS LCA work package received invitations to participate in future trainings organised by TranSensus. These workshops are designed to equip participants with advanced knowledge and skills in life-cycle assessment methodologies. By integrating the harmonised LCA approach proposed by TranSensus in the future, RHINOCEROS has the possibility to contribute to the broader goals of this coordination and support initiative and potentially influencing policy development.
Discussions about LCA raised additional questions about life-cycle costing (LCC). Although not comprised in the scope of work of TranSensus, future guidelines will include also recommendations on how to tackle LCC in common approach. TranSensus will continue publishing reports and guidelines towards the end of this year. Among other topics, these deliverables will address:
- Modelling technology penetration in the market
- Recommendations on how to model the energy mix for sensitivity analysis
- Various use cases, RHINOCEROS being a potential candidate for this category
Discover TranSensus deliverables
When it comes to recycling lithium-ion batteries (LiBs), safety and efficiency are paramount. Classified as hazardous waste under EU legislation, spent LiBs pose significant risks, primarily due to their state-of-the-art (SoA) non-aqueous electrolytes. This complex mixture, which includes conductive salts dissolved in organic solvents and additives, is flammable, volatile, and toxic. By their very nature, the uncontrolled release of these components can harm the environment and endanger workers in recycling plants. Additionally, electrolyte residues in LiB waste streams represent a financial burden for the recycling industry since they are still classified as hazardous waste. Therefore, safely recovering the electrolyte is crucial for developing a secure recycling process.
One promising alternative to traditional methods like vacuum vaporization is supercritical carbon dioxide (ScCO2) extraction. The easily adjustable properties and excellent mass-transfer characteristics of ScCO2 make it potentially ideal for selectively extracting electrolyte components from LiB waste, resulting in purified extraction products. Previous research has demonstrated that non-polar electrolyte solvents like dimethyl carbonate (DMC) and ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC) can be extracted using low-density CO2.
Recent results reported by the research team at University of Chalmers (CHA)have shown that by gradually increasing pressure and temperature conditions, more polar electrolyte components such as ethylene carbonate (EC), and propylene carbonate (PC) can also be successfully extracted. However, selective extraction of solvents remains a challenge, requiring further thermodynamic and kinetic data to optimise the process.
Modelling the extraction behaviour allows the designing of an optimised extraction process that achieves high purity solvents. This high purity enables the recycling industry to either resell the solvents for other uses or even reuse them in battery production, making the process more sustainable and economically viable.
Discover the scientific publication
Work package (WP) 6 partners, notably ECO RECYCLING (IT) team, have completed the first version of the simulations of various hydrometallurgical processes. These tools are essential for the next scaling step since they provide a first version of the material and energy balance. In addition, these simulations make it possible to estimate the time needed to complete a production cycle, to define potential bottlenecks at each step and, above all, to define the necessary equipment and their sizing in order to produce 10kg/day of battery active material.
In parallel with the process simulations, WP6 research team compiled an equipment inventory to assess the potential use of the facilities currently available at JGI-HYDROMETAL (BE), as part of the RHINOCEROS project. This timely inventory will help the partners to identify the additional equipment requirements necessary to properly equip the pilot plant for the scale-up process. Work is underway to best prepare the construction of the future pilot.
There is an undeclared competition for better, more efficient batteries which pushes researchers to continue developing new methods for extracting and synthesising electrodic materials.
Recovery of lithium as battery grade material
Lithium (Li) is a key component in batteries and scientists involved in the RHINOCEROS Project have been exploring ways to extract it from recycled materials from used batteries known as “black mass” (BM). But one of the challenges scientists are facing is the reduction of fluoride content in extracted Li. Researchers at KIT tested their mechanochemical process for extracting Li from various BM samples provided by partners ACC and TES. Their experiments engaging reactive milling coupled with various reactive agents aimed to reduce the fluoride content of the aqueous solution. These tests showed that using magnesium as a reactive agent yielded most promising results for Li extraction.
Progress in Lithium-Manganese battery materials and Advancements in reduced graphene oxide production
Research team at Sapienza Univ. of Rome (UoS) has been making progress in developing lithium-manganese-rich materials for battery applications. These materials were produced using an integrated hydrometallurgical process, which includes the production of reduced graphene oxide and a co-precipitation method that leads to the formation of lithium-manganese-rich cathodes. The resulting cathode materials are currently undergoing extensive physicochemical and electrochemical characterizations.
For the synthesis of reduced graphene oxide, the researchers compared two methodologies and observed differences in productivity. These differences are now being investigated to determine whether they are influenced by the thermal pre-treatment of the graphite or by the role of metals present in different oxidation states. The use of mechano-chemically treated powder has demonstrated remarkable productivity, reaching approximately 80%.
Enhanced solvometallurgical processes
As evoked by its name, solvometallurgy uses solvents to extract metals. Researchers at TEC have been optimising the process, using additives as copper (Cu) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) when necessary, achieving a high recovery rate of >95%. However, the process also increased the dissolved Cu content, which required additional steps to reduce it. Researchers are now exploring methods like cementation or electrodeposition to recover and reuse the dissolved Cu. The deep eutectic solvents (DES) were already regenerated and reused, result which could bring a positive impact on the process sustainability assessment.
Direct recovery of battery materials
The Gas-Diffusion Electrocrystallisation (GDEx) technology allows the one-step recovery of metals and synthesis of new materials with high added value. In the framework of the RHINOCEROS project, the research team at VITO has been focusing on optimising the GDEx technology to achieve the selective recovery of nickel (Ni), manganese (Mn), and cobalt (Co), contained in leachates from black mass and achieved 90 % extraction of Ni, Mn and Co. This two-step GDEx process facilitated the removal of all the impurities such as Cu, Fe from the leachate solution. Using the GDEx process, VITO researchers have successfully synthesised Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) materials and spinel-type nanostructures from the synthetic solutions. The LDH materials were lithiated and LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 (LNMCO811) was synthesised, which could be used as a cathode active material for lithium-ion batteries (LiBs). The results obtained with synthetic solutions portray the potential of the method to obtain relevant active cathode materials out of leachate solutions.
Recovery of materials from low concentration waste streams
Aiming towards a zero-waste strategy for the recovery of metals from battery refining waste waters, LEITAT is working on the development and evaluation of novel polymer inclusion membranes (PIM). PIMs are a type of liquid membrane in which the liquid phase, the extractant, is held within a polymeric network. The interest in these membranes has been growing exponentially over the past few years as an alternative separation technique to conventional solvent extraction.
During the previous six months, the team at LEITAT have been investigating two types of membranes that have shown high selectivity, recovering manganese (Mn) and cobalt (Co) from mixed metal solutions. In their future research, LEITAT will use these membranes in combination to ensure increased selectivity of targeted metals.
Optimising lithium carbonate recovery
Lithium carbonate(Li₂CO₃) is another critical material for batteries, and researchers at TEC and LEITAT are working to optimise its recovery from various solutions. This involves fine-tuning the conditions for Li₂CO₃ precipitation, including the influence of pH and the presence of other cations. Tests are currently conducted with both synthetic solutions and real leachates to ensure the effectiveness of the process. Additionally, efforts are underway to automate the recovery process, which includes assembling elements for pH monitoring and CO2 bubbling systems.
Bringing innovations to market
To bring these innovations to market, researchers are preparing to scale up their processes. This involves a selective process based on data collection, life cycle assessment (LCA) and life cycle cost (LCC) analysis, to ensure the best technological routes are chosen to be further upscaled and meet the production demands.
Researchers at University of Agder (UiA) are working on the automated sorting and dismantling of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) that facilitates their reuse for second life applications.
During the first reporting period, UiA designed a simulator within a virtual environment, which allowed researchers to collect necessary data and parameters, and additionally identify potential bottlenecks that may occur in the actual disassembly process. Beyond collecting data without any physical experiment, the simulation environment brings the benefit of being cost- and time-efficient, allowing for safe and flexible robotic programming without disrupting the production.
According to the simulation environment that covers the entire disassembly process, from automated discharging to sorting, the entire process can run with a total duration spanning between 12 and 14 minutes. The detailed results of this activity will soon be publicly available in a new scientific paper titled addressing the evaluation of deep reinforcement learning for job shop problems.
During the past six months, UiA researchers have constructed a virtual simulator to train the Machine Learning (ML) algorithms. Deep learning methods have already been applied for the Job Shop problem for finding the optimal disassembly sequence when the dependence matrix is known. Next development steps will entail training the algorithms to enable automatic disassembly of Electric Vehicle (EV) batteries without prior knowledge, while optimising procedures and enhancing safety.
© AdobeStock Photos
